Pulp Therapy
334 - Antibacterial Assessment of Children’s Afrin® Against Rothia dentocariosa

Roman M. Garcia, DMD, MPH
Pediatric Dental Resident
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN
University of Minnesota
Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States- RJ
Robert Jones, DDS, PhD
University of Minnesota
- DK
Dhiraj Kumar, PhD
University of Minnesota
Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States 
Jeffrey Karp, D.M.D., M.S.
Residency Program Director
University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN
School of Dentistry , University of Minnesota
Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
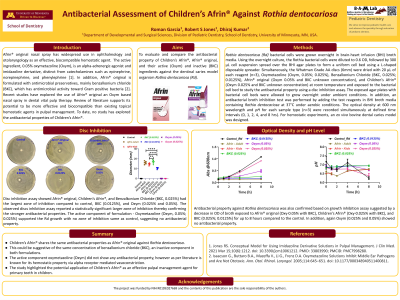
Purpose: To evaluate and compare the antibacterial and hemostatic properties of Children’s Afrin®, Afrin Original®, Oxymetazoline, and Benzalkonium Chloride against Rothia dentocariosa.
Methods: Rothia bacterial cells were grown overnight in brain-heart infusion (BHI) broth media. The bacterial cells were diluted to 0.6 OD at 600 nm, followed by cell suspension spread over agar plates. Whatman discs (6mm) were dried with each reagent, Oxymetazoline (Oxym, 0.05%; 0.025%), Benzalkonium Chloride (BKC, 0.025%; 0.0125%), Afrin Original® (Oxym 0.05% with BKC), and Children’s Afrin® (Oxym 0.025% with BKC) and exposed to the bacterial cell bed to study the antibacterial property using a disc inhibition assay. An antibacterial broth inhibition test was performed. The optical density at 600nm and pH for each sample type were recorded at defined time intervals (0, 1, 2, 4, and 8 hrs).
Results: Disc inhibition assay showed Afrin Original®, Children’s Afrin®, and Benzalkonium Chloride (0.025%) had the largest zone of inhibition compared to control, BKC (0.0125%), and Oxym (0.025% and 0.05%). The observed discs inhibition assay reported a statistically significant larger zone of inhibition, confirming the stronger antibacterial properties. A decreased OD of broth exposed to Benzalkonium Chloride (0.025%; 0.0125%), Afrin Original® (Oxy-0.05% with BKC), and Children’s Afrin® (Oxy-0.025% with BKC) for up to 8 hours compared to the control and Oxymetazoline (0.05%; 0.025%).
Conclusion: Children’s Afrin® shares the same antibacterial and hemostatic properties of Afrin Original®. The study highlighted the potential application of Children’s Afrin® as an effective pulpal management agent for primary teeth care in kids.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number: Acknowledgements: This work was supported by NIH grant R01DE027669

.jpg)