Sedation
350 - Using the BIS monitor to determine Peak Onset of Sedation

Julia Kollesar, DDS
Pediatric Dental Resident
University at Buffalo
University at Buffalo
Buffalo, New York, United States- JH
Julie Heard, n/a
University at Buffalo
- JM
Jonathan Malinovsky, BS
University Pediatric Dentistry
- CH
Christopher Heard, MD, MBChE, FRCA
University at Buffalo
- AL
Allana Langen, BS
University Pediatric Dentistry
- LP
Lauren Pernick, DDS
University at Buffalo
- RP
Ravi Piryani, MD
University Pediatric Dentistry

Christopher Heard, MD
Anesthesiologist
University at Buffalo, New York
Buffalo, New York, United States- TT
Tammy Thompson, DDS
University at Buffalo School of Dental Medicine
Buffalo, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
Purpose
Pharmacokinetic models are used to predict plasma drug concentrations which considered to be the drug level, for example, in the brain for sedation agents. More recently a new concept of effect site concentration is now considered a better model, takes into account drug entry and drug action delay effect (receptor, enzymatic, membrane). This constant Ke0, can be calculated theoretically using complex mathematics or more simply by measuring the time to peak effect from a bolus. The BIS monitor is a multi-processed EEG that displays the depth of hypnosis as a number 1-100 (Deep coma to awake).
The aim of this study is to estimate the time to peak effect in children for boluses of Midazolam, Fentanyl and Propofol using the BIS monitor to determine the degree and time to peak effect.
Methods
For two age groups of children (A: 11 to 14 years and B: 15-17 years) after the BIS monitor is applied, a bolus of sedative which is part of their scheduled deep sedation regimen is given and the BIS monitor readings are recorded. Once it has reached its nadir the rest of the sedation plan is given and the procedure completed.
Results
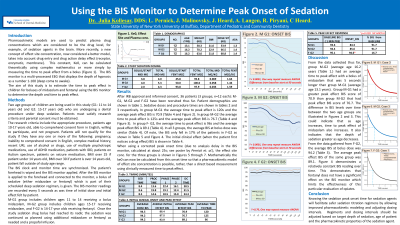
We have recruited 17 patients so far. In Group B (n=12) Midazolam bolus, the average time to peak effect is 125 seconds, average minimum BIS is 77, average procedure BIS 62.
Conclusion
Knowing the sedation peak onset time will facilitate safer sedation titration regimens by allowing improved pharmacokinetic modeling and adjusting dosing intervals.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number:

.jpg)