Sedation
Developing a Pediatric Dental Procedure Score Dority K, Heard C, Heard J, Malinovsky J State University of New York University at Buffalo, Department of Pediatric and Community Dentistry
416 - Developing a Pediatric Dental Procedure Score

Katherine C. Dority, DDS
Pediatric Dental Resident
University at Buffalo/Women and Children’s Hospital of Buffalo, Buffalo, NY
University at Buffalo Department of Pediatric and Community Dentistry
Delmar, New York, United States- JH
Julie Heard, Student
University Pediatric Dentistry
- JM
Jonathan Malinovsky, B.S.
University Pediatric Dentistry

Christopher Heard, MD
Anesthesiologist
University at Buffalo, New York
Buffalo, New York, United States- TT
Tammy Thompson, DDS
University at Buffalo School of Dental Medicine
Buffalo, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
Purpose:
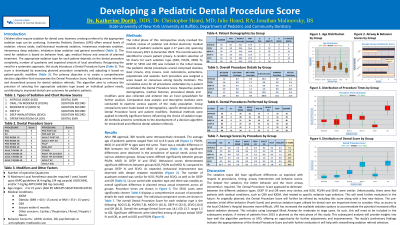
Children often require sedation to facilitate dental care. There are several sedation options and various factors that must be considered, including extent of dental procedure, age, behavior and medical co-morbidities. The aim of this retrospective study is to create a decision algorithm for indicated sedation type based on the pediatric dental score and specific patient modifiers.
Methods:
We will randomly review sedation and dental electronic medical records from pediatric patients ages 2-17 years old from January 2021 to December 2022. The sedation types reviewed (50 charts each) were nitrous oxide (NO), oral/intranasal moderate sedation (PO/IN), intravenous moderate sedation (MOD), intravenous deep sedation (DEEP), inhalation deep sedation (SEVO) and general anesthesia (GA). The pediatric dental procedures scored include stainless steel crowns, strip crowns, resin restorations, extractions, pulpotomies and sealants. Each procedure was assigned a score based upon faculty consensus; the sum of which is the dental score for each patient. Patient demographics and medical histories were also collected.
Results:
We reviewed 97 records thus far. The average age ranged from 4.8-7.8 years old. The overall dental score for NO, PO/IN, SEVO, MOD, DEEP, GA were: 7.5, 9.7, 9.6, 16.5, 30.5, 38.2 respectively. ANOVA analysis confirmed that NO score was different from MOD, DEEP and GA and MOD score was different from SEVO, DEEP and GA.
Conclusion:
Early evaluation of the dental score appears to be appropriate. Once the current chart review is completed, we will create the decision algorithm and re-evaluate with a further 300 chart review.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number:

.jpg)