Special Health Care Needs
556 - The Oral Microbiome in Pediatric Hematopoietic Cell Transplant Recipients
.jpeg.jpg)
Kyulim Lee, DMD, MS, PhD
Faculty
The Ohio State University College of Dentistry, Columbus, OH and Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH
The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
Columbus, Ohio, United States- CB
Cliff Beall, MS, PhD
The Ohio State University College of Dentistry
- SH
Shahr Hashimi, BS
The Ohio State University College of Dentistry
- EL
Eugene Leys, PhD
The Ohio State University College of Dentistry
- JT
Janice Townsend, DDS, MS
The Ohio State University College of Dentistry and Nationwide Children's Hospital
- AK
Ashok Kumar, DDS, MS
The Ohio State University College of Dentistry and Nationwide Children's Hospital
- RB
Rajinder Bajwa, MD
Nationwide Children's Hospital

Ann L. Griffen, DDS, MS
Professor
The Ohio State University College of Dentistry, Columbus, OH and Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH
Columbus, Ohio, United States- KH
Kim Hammersmith, DDS, MPH, MS
Program Director
The Ohio State University College of Dentistry, Columbus, OH and Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH
Columbus, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
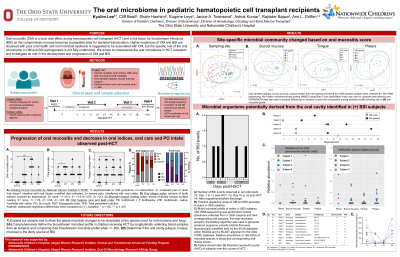
Purpose: Oral mucositis (OM) is a toxic side effect during hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) and a risk factor for bloodstream infections (BSI). Although oral microbial dysbiosis is suggested to be associated with OM and oral bacterial species are implicated in BSI, majority of this research is limited to adults. We evaluated the oral health of pediatric HCT recipients and characterized their oral microbiome during OM and BSI development.
Methods: Ten subjects were followed longitudinally during HCT therapy. Oral indices (gingivitis, plaque, tongue coating) and mucositis grades were recorded. Site-specific oral samples (plaque, mucosa, tongue) and BSI-positive blood samples were collected for 16S rRNA sequencing. Beta-diversity was measured using Bray-Curtis dissimilarity for sampling sites and PERMANOVA was used to examine bacterial community composition change as OM developed. Amplicon sequence variants generated through DADA2 allowed high resolution identification and tracking of organisms between oral niches and blood.
Results: Progression of OM and changes in oral indices was observed as subjects underwent HCT. Distinct microbial communities colonized different oral sites (P=0.001) and site-specific microbial communities changed based on OM grade (plaque P=0.023, buccal mucosa P=0.006, tongue P=0.041). Polymicrobial profiles containing microbial species common to the oral cavity were identified in the bloodstream of subjects with BSI.
Conclusions: Distinct microbial signatures were observed in plaque, mucosa and tongue, and these communities shifted as OM developed. High resolution tracking linked BSI to an oral source. These data provide the foundation for future mechanistic studies and development of preventive therapies for bloodstream invasive oral microbes.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number: Research supported by Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Abigail Wexner Research Institute, Clinical and Translational Intramural Funding Program, IFPAWRI022023

.jpg)