Sedation
Retrospective review of deep inhalational Sevoflurane sedation for pediatric oral surgery patients.
419 - Retrospective Review of Deep Inhalational Sevoflurane Sedation For Pediatric Oral Surgery Patients

Ahmad Alnuaimy, DDS
Pediatric Dental Resident - PGY2
University at Buffalo/Women and Children’s Hospital of Buffalo, Buffalo, NY
University at Buffalo
buffalo, New York, United States- JH
- CH
- TV

Christopher Heard, MD
Anesthesiologist
University at Buffalo, New York
Buffalo, New York, United States- TT
Tammy Thompson, DDS
University at Buffalo School of Dental Medicine
Buffalo, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Co-Author(s)
Research Mentor(s)
Program Director(s)
Purpose:
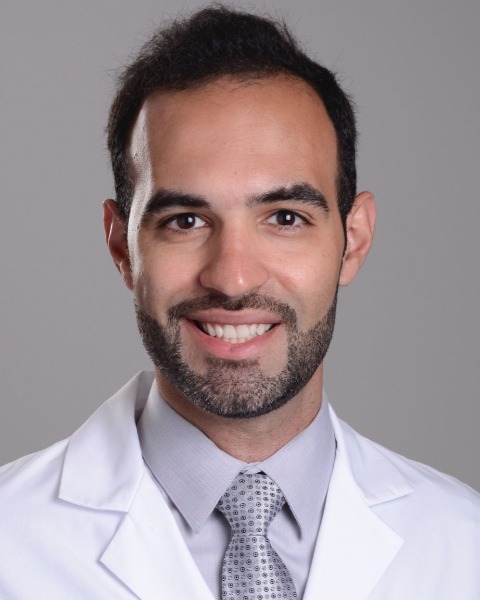
We have previously investigated the use of deep inhalation Sevoflurane sedation for pediatric dental restorations. We found that this approach was not only safe and efficacious but also well-received by both parents and children, given the absence of the need for IV placement. Building upon this success, we have extended the application of this technique to short oral surgery procedures. Treatments that often necessitate the expertise of an Oral Surgeon (mostly complicated adult molar extractions, multiple orthodontic extractions). The current study adopts a retrospective design, aiming to review the efficacy and safety of deep inhalation Sevoflurane sedation. We anticipate airway scores to fall within the standard range of 5-6, with 3-4 being considered acceptable and 1-2 not acceptable.
Methods:
After IRB approval we have identified 124 charts for retrospective review. This will include patient demographics, Sedation outcomes including procedure success, patient’s behavior score and airway score.
Results:
We have reviewed 32 charts so far. The average age: 10.9 years, average BMI: 20.0, average Sevoflurane time 7.8 minutes, average procedure time 4.5 minutes, average airway score is 4.8 and the average behavior score is 10. The median was 1 dental procedure (range 1-6).
Conclusion:
In this preliminary analysis, our early findings suggest that the results are demonstrating comparable efficacy and safety to our previous study involving dental restorations in pediatric patients. Ongoing review of the remaining charts will provide a more comprehensive understanding of the outcomes and further validate the benefits of deep inhalation Sevoflurane sedation in oral surgery procedures.
Identify Supporting Agency and Grant Number: N/A

.jpg)